Meeting Information
Date: 3/29/2017
Time: 2pm
Location: JC311D
Agenda
Digital Analytics Specialist Position
- Website
- Training
- Explainers/How-To’s
- Individual consultations/assistance upon request
- Resources
- Documentation of existing university-owned Google Analytics properties, including contact info, etc.
- Organization of university-owned Google Analytics Accounts/Properties/Views, including consistent naming conventions, settings, etc.
General Web Analytics
Google Analytics Academy
GA Interface Changes
https://analytics.googleblog.com/2016/10/improvements-coming-to-google-analytics.html
- When logging-in, GA will open to the last view that you accessed.
- You can now set a default date range in your user settings.
- All custom objects (dashboards, reports, shortcuts, alerts) are grouped together under the Customization tab.
- Improved view selector. Old ‘index’ view is hidden. (You can actually still get to it if you go to the User Settings window and then hit ‘Cancel’.)
![]()
- Customization: Custom objects (dashboards, reports, shortcuts, alerts) you have created.
- Real-Time: What is going on on your website – right now.
- Audience: Who is looking at your website?
- Acquisition: How are they finding your website?
- Behavior: What are they doing on your website?
- Conversions: Are they doing what you want them to do on your website (goals, etc.)?
Property Moving
You can now move GA properties between two GA accounts!
More info: https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/6370521?hl=en
- To move a property, you must have ‘Manage Users’ and ‘Edit’ permissions on both accounts!
Roll-Up Update
Development Websites
Please don’t put development websites in the roll-up.
In fact, you probably shouldn’t implement web analytics on development websites at all. If you do, be sure to add an annotation when you publicly launch the site.
Hostname/Business Unit List
What websites are being collected in the roll-up, and who do they belong to?: Hostname list
Please confirm your websites in this list and let me know if any are categorized incorrectly, or if any of your websites are not categorized at all.
New Websites in Roll-Up
CVPA websites coming soon.
Here are the new websites sending data to the roll-up since the last meeting:
| Hostname | Business Unit | Business Unit Subgroup | Import Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| financialaid.gmu.edu.googleweblight.com | EM | 3/27/2017 | |
| givingday.gmu.edu | Alumni-Devel | 3/27/2017 | |
| jijua.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| law.gmu.edu | LAW | 3/27/2017 | |
| ls.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| nova.rambler.ru | 3/27/2017 | ||
| ocpe.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| robinson.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| search1.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| seor.vse.gmu.edu | VSE | 3/27/2017 | |
| sol-new.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| staging.aimva.org | 3/27/2017 | ||
| superman.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| vse-dev.preprod.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| wjmc.gmu.edu | EM | 3/27/2017 | |
| wjmc.gmu.edu.googleweblight.com | EM | 3/27/2017 | |
| wsp.gmu.edu | EM | 3/27/2017 | |
| www.ocpe.gmu.edu | 3/27/2017 | ||
| wyse.gmu.edu | EM | 3/27/2017 |
Moving to Tag Manager
In the medium term, we are looking at moving to using Google Tag Manager (GTM) to implement Google Analytics.
Advantages:
- We won’t have to edit JavaScript code on the site to make configuration changes. (Other than implementing the GTM code the first time.)
- It will be easier to implement custom event tracking.
- It will be easier to implement roll-ups. It can be done in the GTM interface rather than editing JavaScript.
- This should enable us to send event data to multiple GA properties, not just pageview data.
Disadvantages:
- Less cool JavaScript to write.
Implementing GA site search analytics on Drupal - Mandy Richburg
This applies to everyone in Drupal – or who will be moving to Drupal.
The problem is that the search term is not sent via a URL query parameter.
Account: Web Communications
Property: http://www2.gmu.edu
View: Test View
Filters:
- Get the search term from URL and store it in ‘Search Term’ field:
“/search/(.*?)((?=\/)|(?=\?))”
This regex will fire on any pages which contain the string “/search/” and will then extract whatever term comes next (up to the next slash or question mark, or the end of the URL) and store it in the ‘Search Term’ field. - Strip site search terms from URL (‘Request URI’ field).
Show example of search URLs in Behavior -> Site Content -> All Pages report. This aggregates all search URLs. Compare with regular view on which the search term fixes have not been made. Search URL activity is split.
Site Search Ideas
Identify differences in searches by originating page
Where someone is on the site makes a big difference in what they are searching for.
Examples:
Account: Web Communications
Property: http://www2.gmu.edu
View: Test View
Report: Behavior -> Site Search -> Search Pages
Click on homepage (/). Top results: “people finder”, “library”, “patriot web”, “Mason live”…
Click on Admissions and Aid page (/admissions-aid). Top results: “Tuition”, “tuition”, “tuition and fees”, “fees”…
This may help determine if there is something on your site people are having trouble finding.
Search trends over time
You could pull reports of top search terms periodically (perhaps weekly) to see trends.
I am working on a Google Sheets app to automate this.
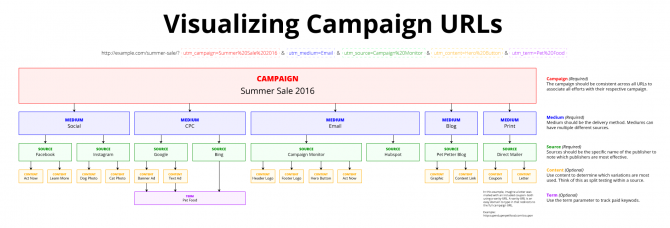
Discussion: Social Media Campaign Tagging
We have previously discussed coordination of email link tagging. See previous session notes here.
What is Campaign Tagging?
You can use campaign parameters to identify how traffic reaches your website. Campaign information is appended to your HTML links to provide additional, customized data.
When someone follows a link to your website, GA records the hits and populates the standard GA dimensions/metrics for the hit in its database.
Campaign tagging basically give you an easy, self-service way to customize the data loading into in a few key dimensions which are used in your GA reports.
Social Media Campaign Tagging
Add campaign parameters to the links you use on social media.
Why? If we want to find out how effective social media links are at driving traffic, we need to include campaign parameters that tell our analytics which link the person followed to get to our website.
Campaign parameters include: “medium”, “source”, “campaign” (and “content” and “term”).
For social media links, the values should be:
- Medium: “social”
- Source: indicates the source of where the user found this link. Examples: “facebook”, “twitter”, etc.
- Campaign: what messaging goal or initiative does this particular link support? Examples: “graduation”, “events”, “athletics”, “alumni”, etc.
- Content: typically used to differentiate different ads used in the same campaign. I would recommend using this to specify the particular communication if desired.
- Term: typically used for paid advertising to store the keyword that caused the ad to display. I would recommend not using this parameter.
Notes
To establish consistency, please use all lowercase characters for your campaign parameters.
You generally don’t need to include the date in your campaign parameters. Typically the date of the communication is pretty clear from looking at the timeline in Google Analytics.
Example: Linking to the Today@Mason page from Facebook
No campaign parameters: www2.gmu.edu/today-mason
With campaign parameters: www2.gmu.edu/today-mason?utm_medium=social&utm_source=facebook&utm_campaign=events
Goals Overview - Nicole Hitpas
- Why should you use goals?
- Intermediate goals/subgoals
- Examples of goals
- What are you goals?